Types of Telecentric Lenses
The classification of telecentric lenses depends on the aperture’s position—whether at the entrance, exit, or both. Each type serves distinct imaging needs:
1. Object-Space Telecentric Lenses
- Design Principle: Entrance pupil placed at infinity.
- Key Benefit: Consistent object size regardless of distance.
- Features: Fixed working distance, orthographic projection, reduced parallax errors.
- Applications: Microscopy, industrial measurement, and vision systems requiring dimensional stability.
- Note: Larger and more expensive than other lens types due to complex construction.
2. Image-Space Telecentric Lenses
- Design Principle: Exit pupil positioned at infinity.
- Key Benefit: Image size remains constant even when the object distance changes.
- Applications: Ideal for image sensors with microlens arrays, digital cameras, and systems sensitive to angle-of-incidence variations.
3. Bi-Telecentric Lenses
- Design Principle: Both entrance and exit pupils are set at infinity.
- Key Benefit: Superior measurement precision compared to single-sided telecentric lenses.
- Applications: Optical lithography, semiconductor inspection, and high-end vision systems.
- Performance: Offers natural afocal behavior, making them the gold standard in dimensional metrology.
Telecentric Lens Design Principles
The primary goal of telecentric lens design is to minimize magnification errors caused by variations in the object-to-lens distance. Depending on the design (object-side, image-side, or bi-telecentric), unique optical pathways are created:
- Object-Side Telecentric Light Path: Chief ray in object space runs parallel to the optical axis, ensuring accurate object measurements.
- Image-Side Telecentric Light Path: Chief ray in image space remains parallel to the axis, maintaining consistent focus across the image sensor.
- Bi-Telecentric Light Path: Combines both object and image telecentricity for maximum accuracy in vision measurement and detection.
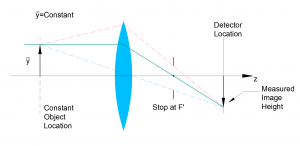
Object Space Telecentric Light Path
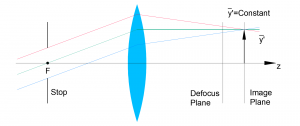
Image-Side Telecentric Light Path
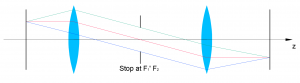
Bi-Telecentric Light Path
How to Choose the Right Telecentric Lens
Selecting the right telecentric lens design requires careful consideration of system requirements:
- CCD/Sensor Size Compatibility:
Ensure the lens supports a sensor size equal to or larger than your camera sensor.
- Magnification (Mag) Calculation:
- Confirm object size and sensor size.
- If no exact magnification is available, choose a slightly smaller one to cover the full object area.
- Working Distance (WD) & Lens Size:
Verify that the WD and physical lens size fit seamlessly into your system design.
- Additional Performance Factors:
Consider distortion levels, depth of field (DOF), and other application-specific requirements.
Telecentric Lens Applications
- Industrial Machine Vision: Dimensional accuracy for automated inspection.
- Microscopy: Precise imaging without perspective distortion.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: Optical lithography and wafer inspection.
- Metrology Systems: High-accuracy 2D and 3D measurements.
Shanghai Optics: Custom Telecentric Lens Solutions
At Shanghai Optics, we specialize in designing and manufacturing custom telecentric lenses tailored to your exact application. Our lenses are engineered to deliver high accuracy, superior stability, and excellent optical performance.
Explore our custom telecentric lens solutions today and contact us for expert consultation.




