Zinc Selenide (ZnSe) prisms are essential optical components widely used in infrared (IR) applications due to their broad transmission range, low absorption, and excellent optical homogeneity. These prisms serve critical roles in beam steering, image rotation, and dispersion within IR systems, from laser-based instrumentation to thermal imaging devices.
Why ZnSe?
ZnSe is a chemically vapor-deposited material that combines high infrared transmittance (0.6 – 21 μm) with low absorption at CO₂ laser wavelengths (10.6 μm), making it ideal for use in mid- and long-wave IR systems.
Wavelength and Transmission Range Information
ZnSe exhibits a broad transmission range, making it suitable for various IR applications:
- Transmission Range: 0.6 µm to 21 µm
- High Transmission Efficiency: Approximately 70% transmission between 1 µm and 15 µm
- Refractive Index: 2.4028 at 10.6 µm
These properties make ZnSe prisms ideal for systems operating at key IR wavelengths, such as the 10.6 µm emission of CO₂ lasers.
Common ZnSe Prism Types
- Right-Angle Prisms
Used for 90° beam deflection or 180° image rotation. ZnSe right-angle prisms are standard in IR alignment tools and CO₂ laser systems.
- Wedge Prisms
Employed to slightly deviate or steer a beam. These are often used in IR beam combining or beam-splitting assemblies.
- Pellin-Broca and Dispersive Prisms
Utilized in spectrometers and FTIR systems, where precise wavelength separation is required in the mid-IR range.
- Roof Prisms and Dove Prisms
Though less common, ZnSe versions are used in compact thermal imaging systems for image rotation and inversion.
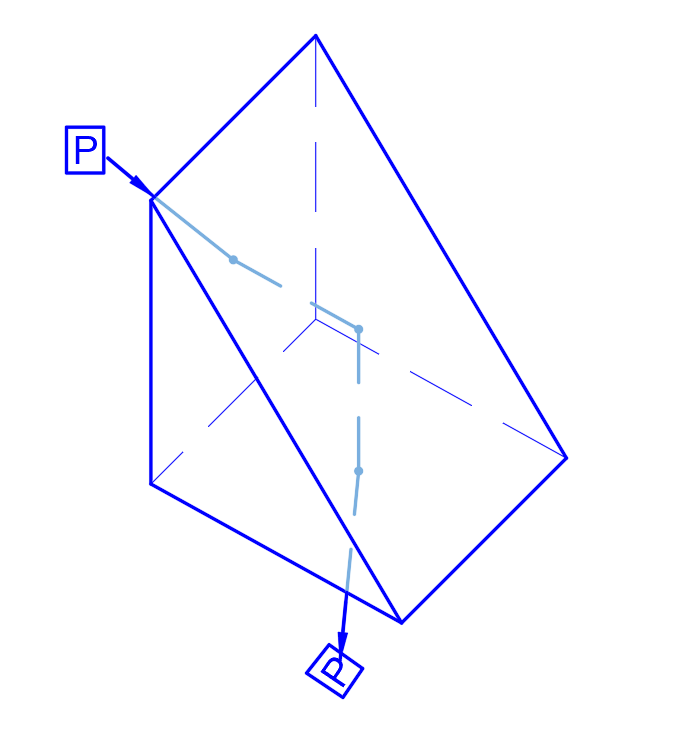
Right Angle Prism
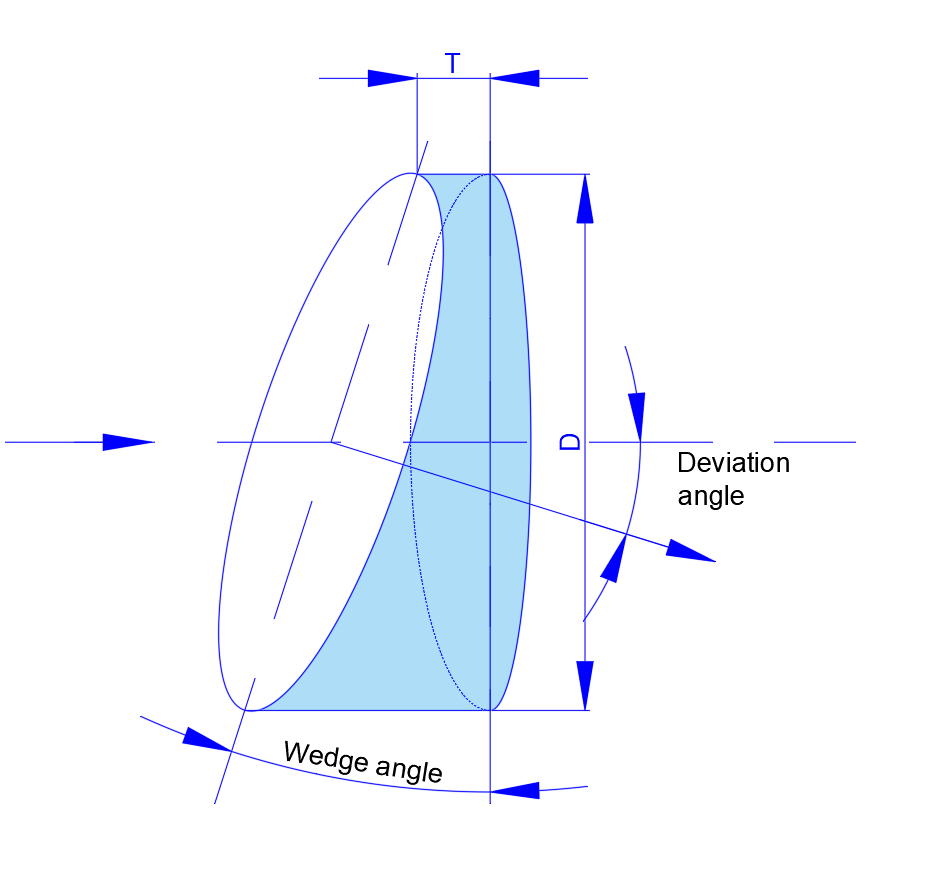
Round Wedge Prism
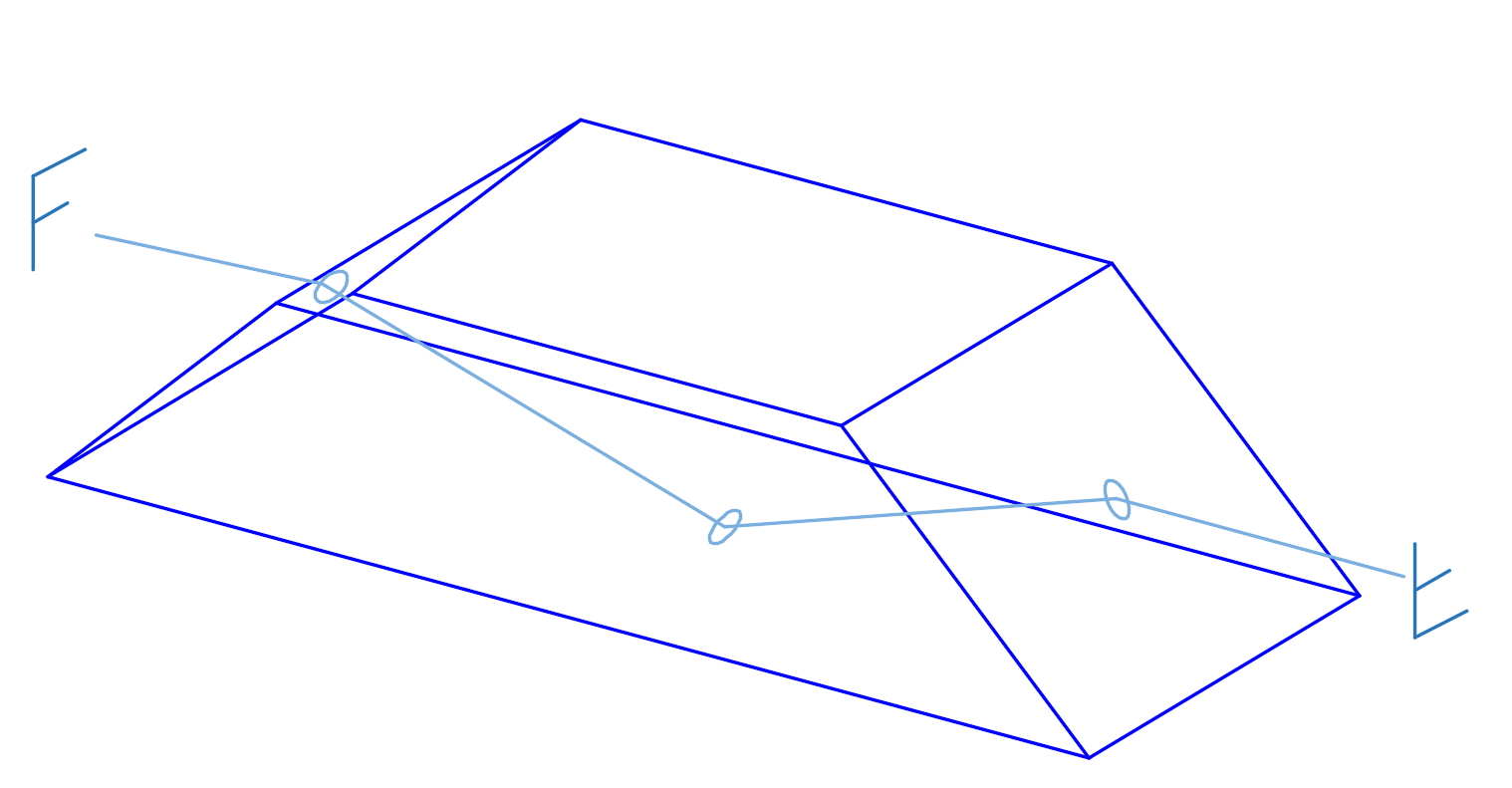
Roof Prism
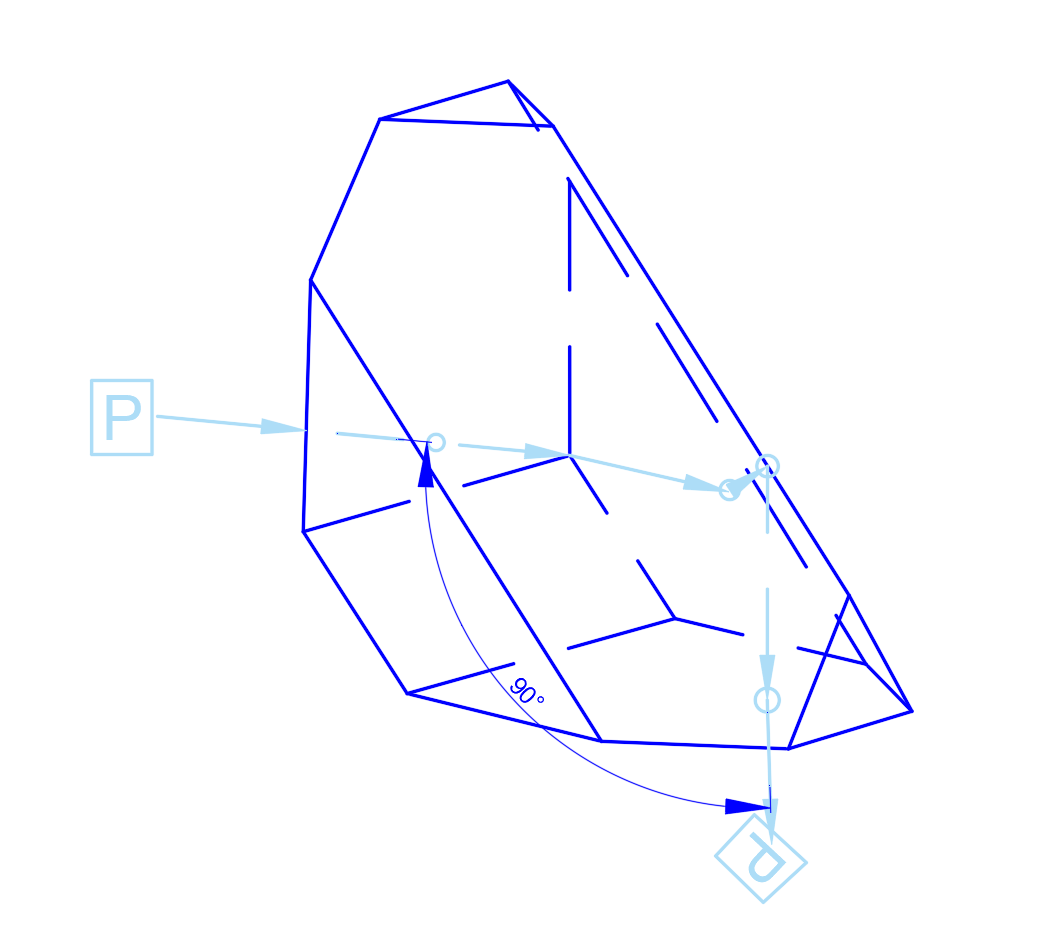
Dove Prism
Manufacturing Challenges
Despite their optical advantages, ZnSe prisms pose several fabrication challenges that require careful consideration throughout the manufacturing process:
- Material Softness and Fragility:
ZnSe is relatively soft (Knoop hardness ~120) and brittle, making it susceptible to chipping, scratching, and microcracks during machining and handling.
- Surface Quality Control:
Achieving high surface flatness and low scatter is difficult due to the material’s tendency to develop sub-surface damage during polishing, especially on steep prism angles or small geometries.
- Coating Adhesion:
The soft, hygroscopic nature of ZnSe creates complications for achieving uniform, durable thin-film coatings. Poor surface preparation or improper coating techniques can lead to delamination or degradation under thermal cycling.
- Thermal Sensitivity:
ZnSe has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion (~7.6 × 10⁻⁶ /K), requiring strict thermal management during fabrication, coating, and use — particularly in high-power laser systems.
- Tight Tolerances on Geometry:
Achieving angular accuracy below 1 arcminute, especially on complex or miniature prism types, challenges even experienced optical manufacturers.
Solutions
To overcome the above challenges, leading manufacturers implement a combination of advanced techniques and strict quality controls, including:
- Precision CNC Grinding with Low-Stress Parameters:
Using ultra-fine diamond tools and optimized feeds/speeds minimizes material stress and edge chipping. Specialized fixturing reduces vibration and handling risks.
- Polishing with Sub-Abrasive Slurries:
Modified pitch polishing with alumina or colloidal silica slurries reduces surface micro-damage. Sub-aperture tools are used for tight radii or steep angles to maintain figure accuracy.
- Cleanroom-Based Coating Facilities:
ZnSe prisms are coated in humidity- and particle-controlled environments using IBS (Ion Beam Sputtering) or e-beam evaporation techniques. Adhesion layers like ZnS or Y₂O₃ are applied to enhance film bonding.
- Optical Metrology and Inspection:
Interferometry, autocollimators, and angle measurement systems are used to ensure <1 arcmin angular tolerances. Surface quality is inspected using both visual and laser scattering methods.
- Protective Packaging and Handling:
All finished ZnSe prisms are handled with soft-tipped tools, and packaged with non-abrasive materials to prevent surface damage during transport and storage.
Applications Across Industries
- Laser Optics:
ZnSe prisms are integrated in CO₂ laser systems for beam manipulation and scanning.
- Thermal Imaging:
Used in IR camera modules for compact light path folding and image correction.
- Spectroscopy:
Dispersive ZnSe prisms are essential in FTIR systems analyzing organic compounds, polymers, and gases.
- Industrial Sensing & Automation:
Integrated into IR sensors for non-contact temperature measurement and process control.
Conclusion
ZnSe prisms provide an effective combination of optical performance and IR transparency for precision systems operating in the mid- to long-wave infrared range. Their wide adoption across defense, medical, industrial, and scientific sectors underscores their versatility. With proper coating and polishing techniques, ZnSe prisms can be custom-tailored to meet the stringent demands of advanced optical systems.
Contact Shanghai Optics today! We’d be more than happy to discuss your projects and how to best bring them to fruition.



